Chain Abstraction
Chain abstraction is one of the flagship use cases of Connext. Chain abstraction allows a dapp to execute logic from any chain without requiring users to switch networks, sign transactions on a different chain, and spend gas on a different chain. This pattern can be used at higher layers to fully abstract chains from the user, removing the need for users to consciously have to think about what chain they are on.
For example, a chain abstraction layer for Aave would involve a simple, two-step process.
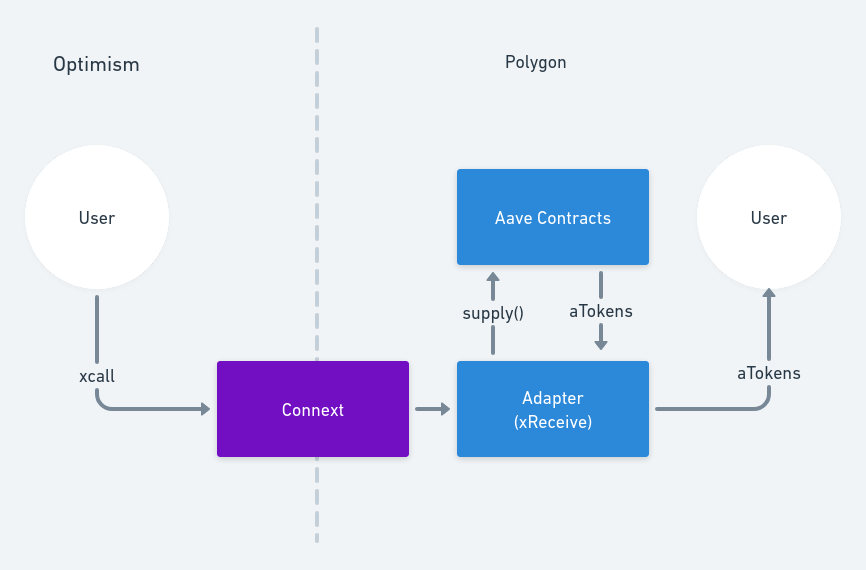
- The Connext SDK is used to construct an
xcalltransaction to be sent by the user on their origin chain. - An adapter contract deployed on the destination chain forwards the
depositcall to Aave.
In the end, no changes are needed on the Aave contracts themselves and cross-chain deposits are enabled for users with maximally simplified UX.
Creating a Chain Abstraction Layer
Chain abstraction consists of two parts: swaps and "forward calls". Swaps are used to convert any asset into a bridgeable asset, and forward calls are used to call a function on a contract on a different chain. The following sections will walk through how to implement these two parts.
Smart Contract Integration
This guide will cover a contract workspace that is using Foundry.
Installation
After your Foundry project is set up, you can add the Connext contracts to your project by running the following command to install the connext-integration repository as a submodule:
forge install connext/connext-integration
The library will be installed to lib/connext-integration.
SwapForwarderXReceiver
The SwapForwarderXReceiver is the abstract contract that should be implemented by receiver contracts that follow the chain abstraction pattern.
abstract contract SwapForwarderXReceiver is ForwarderXReceiver, SwapAdapter {
using Address for address;
/// @dev The address of the Connext contract on this domain.
constructor(address _connext) ForwarderXReceiver(_connext) {}
/// INTERNAL
/**
* @notice Prepare the data by calling to the swap adapter. Return the data to be swapped.
* @dev This is called by the xReceive function so the input data is provided by the Connext bridge.
* @param _transferId The transferId of the transfer.
* @param _data The data to be swapped.
* @param _amount The amount to be swapped.
* @param _asset The incoming asset to be swapped.
*/
function _prepare(
bytes32 _transferId,
bytes memory _data,
uint256 _amount,
address _asset
) internal override returns (bytes memory) {
(address _swapper, address _toAsset, bytes memory _swapData, bytes memory _forwardCallData) = abi.decode(
_data,
(address, address, bytes, bytes)
);
uint256 _amountOut = this.exactSwap(_swapper, _amount, _asset, _toAsset, _swapData);
return abi.encode(_forwardCallData, _amountOut, _asset, _toAsset, _transferId);
}
}
Notice that the _prepare function expects a bytes memory _data parameter that will be decoded into:
_swapper: The specific swapper that will be used for the destination swap._toAsset: The asset that should be swapped into._swapData: The encoded swap data that will be constructed offchain (using the Chain Abstraction SDK in the next section)._forwardCallData: The forward call data that the receiver contract will call.
xReceiver Adapter Contract
The xReceiver adapter contract is the adapter contract that integrators build. It is the target of the origin-side xcall and it will receive funds after swaps are completed. This contract will be deployed to the destination chain and will be called by the router network for a "fast path execution".
The contract simply has to inherit SwapForwarderXReceiver and implement the _forwardFunctionCall method. A simple example is shown below.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.13;
import {TransferHelper} from "@uniswap/v3-periphery/contracts/libraries/TransferHelper.sol";
import {SwapForwarderXReceiver} from "../../destination/xreceivers/Swap/SwapForwarderXReceiver.sol";
interface IGreeter {
function greetWithTokens(address _token, uint256 _amount, string calldata _greeting) external;
}
contract XSwapAndGreetTarget is SwapForwarderXReceiver {
IGreeter public immutable greeter;
constructor(address _greeter, address _connext) SwapForwarderXReceiver(_connext) {
greeter = IGreeter(_greeter);
}
/// INTERNAL
function _forwardFunctionCall(
bytes memory _preparedData,
bytes32 /*_transferId*/,
uint256 /*_amount*/,
address /*_asset*/
) internal override returns (bool) {
(bytes memory _forwardCallData, uint256 _amountOut, , address _toAsset) = abi.decode(
_preparedData,
(bytes, uint256, address, address)
);
// Decode calldata
string memory greeting = abi.decode(_forwardCallData, (string));
// Forward the call
TransferHelper.safeApprove(_toAsset, address(greeter), _amountOut);
greeter.greetWithTokens(_toAsset, _amountOut, greeting);
return true;
}
}
The _forwardFunctionCall function unwraps the encoded data which includes the calldata for the function call, the amount of tokens received after the swap, and the token contract address of the asset that was swapped to. The function then forwards the call to the greeter contract, which is a simple contract that just greets the user with a message while transferring some tokens in exchange.
Chain Abstraction SDK
The Chain Abstraction SDK makes the process of creating the _swapData for swaps very simple.
Installation
For installing the SDK, use Node.js v18. You can install the SDK with the following command.
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install @connext/chain-abstraction
yarn add @connext/chain-abstraction
pnpm add @connext/chain-abstraction
getPoolFeeForUniV3
The function getPoolFeeForUniV3 returns the poolFee of the UniV3 pool for a given token pair which would be used in the UniV3 router execution. The poolFee is the fee that is charged by the pool for trading the tokens.
export const getPoolFeeForUniV3 = async (
domainId: string,
rpc: string,
token0: string,
token1: string,
):
The function takes four parameters:
domainId: The target domain ID.rpc: The RPC endpoint for a given domain.token0: The first token address.token1: The second token address.
The function returns a Promise that resolves to a string representing the poolFee of the UniV3 pool.
Example
// asset address
const POLYGON_WETH = "0x7ceB23fD6bC0adD59E62ac25578270cFf1b9f619";
const POLYGON_USDC = "0x2791bca1f2de4661ed88a30c99a7a9449aa84174";
// Domain details
const POLYGON_DOMAIN_ID = "1886350457";
const POLYGON_RPC_URL = "https://polygon.llamarpc.com";
const poolFee = await getPoolFeeForUniV3(POLYGON_DOMAIN_ID, POLYGON_RPC_URL, POLYGON_WETH, POLYGON_USDC);
console.log(poolFee);
getXCallCallData
The getXCallCallData function generates calldata to be passed into xcall. This is the "outer" calldata that contains encoded "inner" calldata which specifies the swap plus the forward call to a target contract on the destination domain.
export const getXCallCallData = async (
domainId: string,
swapper: Swapper,
forwardCallData: string,
params: DestinationCallDataParams,
)
It takes four parameters.
domainId: A string representing the destination domain ID.swapper: A string representing which swapper should be used. It can beUniV2,UniV3, orOneInch.forwardCallData: encoded data for passing into the target contract usingabiencoder.params: An object containing the following fields.{
fallback: string;
swapForwarderData: {
toAsset: string;
swapData: {
amountOutMin: string;
} | {
amountOutMin: string;
poolFee: string;
};
forwardCallData: {
cTokenAddress: string;
underlying: string;
minter: string;
} | {} | {};
}
}fallback: The fallback address to send funds to if the forward call fails on the destination domain.swapForwarderData: An object with the following fields.toAsset: Address of the token to swap into on the destination domain.swapData: Calldata that the swapper contract on the destination domain will use to perform the swap.forwardCallData: Calldata that the xReceive target on the destination domain will use in the forward call.
The function returns the encoded calldata as a string.
Example
const rpcURL = "https://bsc-dataseed.binance.org";
const signer = new Wallet(process.env.PRIVATE_KEY ?? "", new providers.JsonRpcProvider(rpcURL));
const signerAddress = signer.address;
// ORIGIN SIDE
const BNB_NATIVE = constants.AddressZero;
const BNB_USDC = "0x8AC76a51cc950d9822D68b83fE1Ad97B32Cd580d";
const amountIn = BigNumber.from("5000000000000000");
const fromAsset = BNB_NATIVE;
const toAsset = BNB_USDC;
// DESTINATION SIDE
const POLYGON_WETH = "0x7ceB23fD6bC0adD59E62ac25578270cFf1b9f619";
const POLYGON_USDC = "0x2791bca1f2de4661ed88a30c99a7a9449aa84174";
const POLYGON_CTOKEN_WETH = "0xD809c769A04246855fee98423B180C7CCa6bF07c"; // https://app.midascapital.xyz/137/pool/5
const midasProtocolTarget = "0x5d7663c5483A46e7794b652aF8f155775E4F390C";
// Params for calldata generation
const POLYGON_DOMAIN_ID = "1886350457";
const POLYGON_RPC_URL = "https://polygon.llamarpc.com";
const target = XReceiveTarget.MidasProtocol;
const swapper = Swapper.UniV3;
const poolFee = await getPoolFeeForUniV3(POLYGON_DOMAIN_ID, POLYGON_RPC_URL, POLYGON_WETH, POLYGON_USDC);
const params: DestinationCallDataParams = {
fallback: signerAddress,
swapForwarderData: {
toAsset: POLYGON_WETH,
swapData: {
amountOutMin: "0",
poolFee: poolFee,
}
},
};
const forwardCallData = defaultAbiCoder.encode(
["address", "address", "address"],
[POLYGON_CTOKEN_WETH, POLYGON_WETH, signerAddress],
);
const callDataForMidasProtocolTarget = await getXCallCallData(POLYGON_DOMAIN_ID, swapper, forwardCallData, params);
const swapAndXCallParams = {
originDomain: "6450786",
destinationDomain: "1886350457",
fromAsset, // BNB
toAsset, // USDC
amountIn: amountIn.toString(),
to: midasProtocolTarget,
relayerFeeInNativeAsset: "1000000000000000", // 0.001 BNB
callData: callDataForMidasProtocolTarget,
};
const txRequest = await prepareSwapAndXCall(swapAndXCallParams, signerAddress);
if (txRequest) {
const tx = await signer.sendTransaction({ ...txRequest });
console.log(`SwapAndXCall tx mined. tx: ${tx.hash}`);
await tx.wait();
}
prepareSwapAndXCall
The prepareSwapAndXCall function prepares SwapAndXCall inputs and encodes the calldata. It returns a providers.TransactionRequest object to be sent to the RPC provider.
export const prepareSwapAndXCall = async (
params: SwapAndXCallParams,
signerAddress: string,
):
It takes two parameters:
signerAddress(required): The address of the signer to send a transaction from.params: An object containing the following fields:originDomain(required): The origin domain ID.destinationDomain(required): The destination domain ID.fromAsset(required): The address of the asset to swap from.toAsset(required): The address of the asset to swap to.amountIn(required): The number of fromAsset tokens.to(required): The address to send the asset and call with the calldata on the destination.delegate(optional): The fallback address on the destination domain which defaults toto.slippage(optional): Maximum acceptable slippage in BPS which defaults to 300. For example, a value of 300 means 3% slippage.route(optional): The address of the swapper contract and the data to call the swapper contract with.callData(optional): The calldata to execute (can be empty: "0x").relayerFeeInNativeAsset(optional): The fee amount in native asset.relayerFeeInTransactingAsset(optional): The fee amount in the transacting asset.{
originDomain: string,
destinationDomain: string,
fromAsset: string,
toAsset: string,
amountIn: string,
to: string,
relayerFeeInNativeAsset: string | undefined,
relayerFeeInTransactingAsset: string | undefined,
delegate: string | undefined,
slippage: string | undefined,
route: {
swapper: string,
swapData: string,
} | undefined,
callData: string | undefined,
}
The function returns a Promise that resolves to a providers.TransactionRequest object to be sent to the RPC provider.
Example
const rpcURL = "https://polygon.llamarpc.com";
const signer = new Wallet(process.env.PRIVATE_KEY ?? "", new providers.JsonRpcProvider(rpcURL));
const signerAddress = signer.address;
const POLYGON_WETH = "0x7ceB23fD6bC0adD59E62ac25578270cFf1b9f619";
const POLYGON_USDC = "0x2791bca1f2de4661ed88a30c99a7a9449aa84174";
const SWAP_AND_XCALL_ADDRESS = "0x697075f4A3Ce358d125281134e98d594D8Bb472e";
const amountIn = BigNumber.from("1000000000000000");
const fromAsset = POLYGON_WETH;
const swapAndXCallParams = {
originDomain: "1886350457",
destinationDomain: "6450786",
fromAsset, // WETH
toAsset: POLYGON_USDC, // USDC
amountIn: amountIn.toString(),
to: signerAddress,
relayerFeeInTransactingAsset: "100000", // 0.1 USDC
};
const wethContract = new Contract(POLYGON_WETH, WETH_ABI, signer);
const gasPrice = "500000000000";
const allowance = await wethContract.allowance(signerAddress, SWAP_AND_XCALL_ADDRESS);
if (amountIn.gt(allowance)) {
console.log(`Approving... amountIn: ${amountIn.toString()}, allowance: ${allowance.toString()}`);
const tx = await wethContract.approve(SWAP_AND_XCALL_ADDRESS, amountIn, { gasPrice });
console.log(`Approve tx mined... tx: ${tx.hash}`);
await tx.wait();
}
const txRequest = await prepareSwapAndXCall(swapAndXCallParams, signerAddress);
if (txRequest) {
const tx = await signer.sendTransaction({ ...txRequest, gasPrice });
console.log(`SwapAndXCall tx mined. tx: ${tx.hash}`);
await tx.wait();
}